How To Make A Data Chart On Microsoft Word 2007
- 18 Comments!

You can use this free online tutorial to learn Microsoft Excel 2007. Click here to start the tutorial. If you are using an older version of Excel, click here for our. Edit Article wiki How to Make a Bar Chart in Word. Two Methods: Word 2013 and Later Word 2007 and 2010 Community Q&A. Open the Microsoft Word program.
How to Make a Graph in Microsoft Excel 2007 for Windows. Graphs are great ways to help audiences understand concepts. Examples of some concepts could be Business data. Knowing how to import data into Microsoft Word from any source, including Excel, PDF files, or other Word documents, can save you a lot of time. We'll show you all.
How to Create an Organization Chart on Microsoft Word. Use Microsoft Word to create a professional org chart in a matter of minutes with this step- by- step guide. The quickest way to illustrate the workflow process at your organization may be to simply scrawl it on a whiteboard, but that means you’ll have to change it every time there’s a promotion or new hire. For an instant way to create, update and distribute your organizational chart, Microsoft Word comes equipped with a tool that automatically generates hierarchical diagrams. All you have to do is add your personnel information and save the file. Launch Microsoft Word.
Use our Tutorial on Microsoft Excel to Create a Chart or Graph at Internet 4 Classrooms, internet resources for teachers and students, children and parents.
Once you have your data entered, the rest.
To add an organizational chart to an existing document, open the file and scroll to the place for the chart. Press “Ctrl+Enter” to add a new page. Otherwise, Word starts a new blank document upon opening. Click the “Insert” tab. Click the “Smart. Art” button on the ribbon, which opens the “Choose a Smart.
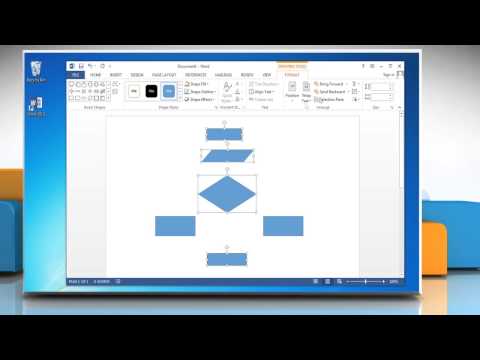
Art graphic” pop- up window. Click the “Hierarchy” link in the left side column. Review the different organizational chart options. These are just the Word defaults – you will be able to change the colors and add rows and boxes in later steps. Double- click a chart, such as “Organization Chart,” that best suits your business. The chart is added to the Word document and a new purple “Smart. Art Tools” tab and ribbon open at the top of the work area.
Click into the first/top box on the chart, which may show “. Type the name and, if desired, title of the highest- ranking person in your organization, such as the CEO, CIO, president or owner. Move to the next box, which branches below the first. Type the name of the next- highest person.
Most Word templates have three boxes on this branch. If you only have one or two people on this branch, click the box and press the “Delete” key.
If you have more than three, click any box on the row, then click the “Add Shape” menu on the ribbon. Click “Add Shape After” to add another box on the same branch. Continue until all persons or job titles on this level of your organization are represented.
Click a box on the second row. Click the “Add Shape” menu and choose “Add Shape Below.” This creates the next, lower level in the organizational hierarchy.
Add boxes, names and titles for each person on this level of your company. Continue to add boxes and rows. Note that as you add boxes, Word will automatically shrink the chart to fit on the page. Assign administrative positions to the persons for whom they work by clicking a box, then clicking the “Add Shape” menu. Click “Add Assistant” and a link is created from the executive to the assistant. Click the “Change Colors” button on the ribbon. Choose a different set of hues from the default Word blue.
You can also change individual colors in the chart. Click a box or click multiple boxes by holding down the “Ctrl” key and then clicking each box to change. Right- click any of the selected boxes and choose “Format Shape.” In the “Fill” window, choose a new color. Click the “File” tab and select “Save As.” Type a name for the organizational chart and select where to save the file. Click the “Save” button. Tip. These instructions apply to Microsoft Word 2.
Word 2. 01. 6. The process is the same in Word 2. Office button instead of the .
Earlier or later versions of Word may have other differences.
Present data in a chart. Learn about charts. Charts are used to display series of numeric data in a graphical format to make it easier to understand large quantities of data and the relationship between different series of data. Worksheet data. 2. Chart created from worksheet data.
Excel supports many types of charts to help you display data in ways that are meaningful to your audience. When you create a chart or change an existing chart, you can select from a variety of chart types (such as a column chart or a pie chart) and their subtypes (such as a stacked column chart or a pie in 3- D chart). You can also create a combination chart by using more than one chart type in your chart.
Example of a combination chart that uses a column and line chart type. For more information about the chart types that you can select in Excel, see Available chart types. Getting to know the elements of a chart. A chart has many elements. Some of these elements are displayed by default, others can be added as needed.
You can change the display of the chart elements by moving them to other locations in the chart, resizing them, or by changing the format. You can also remove chart elements that you do not want to display. The chart area of the chart. The plot area of the chart. The data points of the data series that are plotted in the chart. The horizontal (category) and vertical (value) axis along which the data is plotted in the chart.
The legend of the chart. A chart and axis title that you can use in the chart. A data label that you can use to identify the details of a data point in a data series. Modifying a basic chart to meet your needs. Geforce The Oddity Vst Synth there. After you create a chart, you can modify any one of its elements. For example, you might want to change the way that axes are displayed, add a chart title, move or hide the legend, or display additional chart elements.
To modify a chart, you can: Change the display of chart axes You can specify the scale of axes and adjust the interval between the values or categories that are displayed. To make your chart easier to read, you can also add tick marks to an axis, and specify the interval at which they will appear. Add titles and data labels to a chart To help clarify the information that appears in your chart, you can add a chart title, axis titles, and data labels. Add a legend or data table You can show or hide a legend, change its location, or modify the legend entries. In some charts, you can also show a data table that displays the legend keys and the values that are. Apply special options for each chart type Special lines (such as high- low lines and trendlines), bars (such as up- down bars and error bars), data markers, and other options are available for different chart types.
Applying a predefined chart layout and chart style for a professional look. Instead of manually adding or changing chart elements or formatting the chart, you can quickly apply a predefined chart layout and chart style to your chart. Word provides a variety of useful predefined layouts and styles that you can select, but you can fine- tune a layout or style if it is needed by making manual changes to the layout and format of individual chart elements, such as the chart area, plot area, data series, or legend of the chart. When you apply a predefined chart layout, a specific set of chart elements (such as titles, a legend, a data table, or data labels) are displayed in a specific arrangement in your chart.
You can select from a variety of layouts that are provided for each chart type. When you apply a predefined chart style, the chart is formatted based on the document theme that you have applied, so that your chart matches your organization's or your own theme colors (a set of colors), theme fonts (a set of heading and body text fonts), and theme effects (a set of lines and fill effects).
You cannot create your own chart layouts or styles, but you can create chart templates that include the chart layout and formatting that you want. Adding eye- catching formatting to a chart. In addition to applying a predefined chart style, you can easily apply formatting to individual chart elements such as data markers, the chart area, the plot area, and the numbers and text in titles and labels to give your chart a custom, eye- catching look. You can apply specific shape styles and Word.
Art styles, and you can also format the shapes and text of chart elements manually. To add formatting, you can: Fill chart elements You can use colors, textures, pictures, and gradient fills to help draw attention to specific chart elements. Change the outline of chart elements You can use colors, line styles, and line weights to emphasize chart elements.
Add special effects to chart elements You can apply special effects, such as shadow, reflection, glow, soft edges, bevel, and 3- D rotation to chart element shapes, which gives your chart a finished look. Format text and numbers You can format text and numbers in titles, labels, and text boxes on a chart as you would text and numbers on a worksheet. To make text and numbers stand out, you can even apply Word. Art styles. Reusing charts by creating chart templates. If you want to reuse a chart that you customized to meet your needs, you can save that chart as a chart template (*. When you create a chart, you can then apply the chart template just as you would any other built- in chart type.
In fact, chart templates are custom chart types — you can also use them to change the chart type of an existing chart. If you use a specific chart template frequently, you can save it as the default chart type. Top of Page. Step 1: Create a basic chart. You can add a chart to your Word document in one of two ways: insert a chart by embedding it into your Word document, or paste an Excel chart into your Word document that is linked to data in an Office Excel 2. The main differences between embedded charts and linked charts are where the data is stored and how you update the data after you place it in the Word document. Note: Some chart types require a specific data arrangement in the Excel worksheet.
For more information, see Arrange the Excel worksheet data. Insert a chart by embedding it in your document.
When you embed an Excel chart, information in the Word file doesn't change if you modify the source Excel file. Embedded objects become part of the Word file and, after they are inserted, they are no longer part of the source file. Because the information is totally contained in one Word document, embedding is useful when you don't want the information to reflect changes in the source file, or when you don't want the document recipients to be concerned with updating the linked information. In your Word document, click Insert > Chart. Select the type of chart you want, such as column or pie chart, and click OK. The chart will update to match the data after you finish typing data into one cell and move to the next. Clara Luzia The Long Memory Download.
In Word, click where you want to insert the chart. On the Insert tab, in the Illustrations group, click Chart. In the Insert Chart dialog box, click a chart, and then click OK. Enter your data into the spreadsheet that automatically opens with the chart. The chart will update to match the data after you finish typing data into one cell and move to the next. In Word, click where you want to insert the chart.
On the Insert tab, in the Illustrations group, click Chart. In the Insert Chart dialog box, click a chart, and then click OK. Office Excel 2. 00.
In the Excel window, replace the sample data by clicking a cell on the worksheet and then typing the data that you want. You can also replace the sample axis labels in Column A and the legend entry name in Row 1. Note: After you update the worksheet, the chart in Word will be updated automatically with the new data. In Excel, click the Microsoft Office Button. Save As. In the Save As dialog box, in the Save in list, select the folder or drive that you want to save the worksheet to.